Understanding the Impact of Trauma on Mental Health
Trauma, in childhood or adulthood, significantly impacts mental health and can cause anxiety. Often serving as seeds of psychological disorders like depression, anxiety, PTSD, and stress, traumas are events that uproot psychological stability, implanting distress, fear, and long-term emotional and anxiety-related disruptions. They can be singular incidents or iterative, chronic situations, their effects varying in intensity and manifestation. Interestingly, two individuals undergoing the same traumatic experience may react and cope differently, indicating the impact of personal resilience, support systems and even genetic predispositions.
Studies reveal that trauma can also disrupt the balance of neurochemical systems in our brains, leading to increased stress levels, mood swings, memory problems, and difficulties in emotional regulation. Chronic trauma exposure may lead to changes in brain structure and function, notably in areas linked to emotion, learning and memory. However, trauma, as overwhelming as it can be, is not a life sentence to poor mental health. By understanding its impact and seeking early intervention, individuals can navigate their healing journey more effectively and regain control over their mental health.
Unveiling the Link Between Stress and Anxiety
Exposure to stress is an inescapable aspect of human life. It can manifest in various forms, ranging from intense work-related pressure, personal relationship troubles, financial worries to more intensely traumatic events such as accidents, violence, or severe illness. While stress is a biological response designed to help us react to threatening situations through the famous fight-or-flight response, excessive or long-term exposure to stressful situations can have deleterious effects on an individual’s mental health. In particular, it has been observed to play a significant role in the onset and continuation of anxiety disorders.
Anxiety, however, should not be misconstrued as a mere byproduct of stress. Rather, it is a complex and pervasive mental health issue with a multifaceted etiology. Chronic anxiety often involves feelings of fear, dread, and anticipation of future threats, even in the absence of a current stressful stimulus. Neurobiological research has highlighted the interplay between stress and the development of anxiety, finding that prolonged stress can lead to alterations in brain function and structure, particularly in areas associated with fear and emotion regulation. Thus, while stress and anxiety are distinct phenomena, they are intricately linked, with each having the potential to exacerbate the other, creating a vicious cycle of mental unrest.
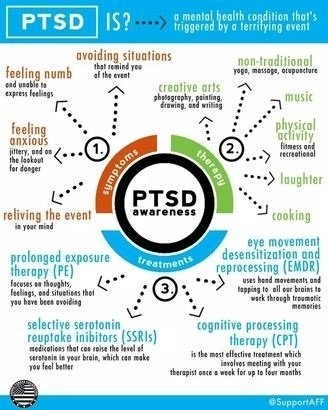
Comprehensive Insight into Trauma-Induced Stress Disorders
Trauma-induced stress disorders, specifically Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (
PTSD) and Acute Stress Disorder (ASD), are prevalent conditions that stem from overwhelmingly distressing or traumatic experiences. They occur when an individual is exposed to a distressing event or series of events leading to an activation of the body’s stress response system, often beyond its ability to manage. This activation may result in an array of mental, physical, and emotional symptoms such as hypervigilance, intrusive thoughts about the traumatic event, difficulty sleeping, and increased irritability.
Understanding these disorders begins with recognizing the different traumatic events that can lead to their development. This could range from experiences of war, natural disasters, personal assaults to childhood abuse. It is key to note that trauma-induced stress disorders aren’t solely an aftermath of monumental events but can also arise from prolonged exposure to high levels of stress in everyday life. Furthermore, individual response to trauma varies greatly, and it’s crucially important to acknowledge this diversity in research and treatment approaches.
Effective Coping Mechanisms for Stress and Anxiety
Stress and anxiety, if unmanaged, can lead to dire consequences for mental health, further causing hindrance to personal growth and well-being. Therefore, individuals ought to adopt suitable coping mechanisms that facilitate stress and anxiety regulation. The incorporation of various strategies, such as consistent exercise, balanced nutrition, and adequate sleep, offer notable results in controlling these mental health afflictions. Engagement in hobbies, being in nature, or even adopting pets are distinctive methods that augment well-being.
Contrarily, the potential benefits of mindfulness practices are emerging as substantial tools for a healthy mind. Through meditation, deep breathing exercises, and targeted yoga, individuals can cultivate a sense of peace and calm, aiding in better stress management. Biofeedback, another noteworthy technique, involves enhancing awareness and control over physiological responses to stress, wherein individuals learn to control factors like heart rate, blood pressure, muscle tension, and other bodily reactions. These methods serve to instil a greater sense of control over one’s mental health, opening doors to improved wellness.
Incorporating Mindfulness Practices for Stress and Anxiety Reduction
Mindfulness, put simply, is the practice of focusing one’s awareness on the present moment, while calmly acknowledging and accepting one’s feelings, thoughts, and bodily sensations. This technique, often used as a therapeutic remedy, has been proven to have significant positive effects on mental health, particularly in the alleviation of stress and anxiety. It fosters a connection with the present, grounding individuals in their current circumstances and aiding them in mitigating negative ruminative thought patterns.
Numerous investigations have revealed that regular mindfulness practices aid in reducing thinning of the prefrontal cortex— an area of the brain related to complex cognitive behavior and decision-making. It also contributes to the reduction of the amygdala, the part of the brain responsible for triggering fear, anxiety, and stress responses. By regular practice, individuals can increase their ability to regulate their emotions, manage stress more effectively, and reduce the risk of mental health disorders. Through directing one’s focus to the present, mindfulness practices serve to improve one’s overall mental health, promoting a more balanced, and less stress-driven, state of existence.
Incorporating mindfulness practices into your daily routine can be achieved in several ways. Here are a few techniques that you might find helpful:
• Meditation: This is perhaps the most common form of mindfulness practice. It involves sitting quietly and focusing on your breath, an image, or a simple mantra to help clear your mind.
• Mindful Eating: Paying attention to what and how you eat can transform the act of eating from a mindless task into a fulfilling experience. Notice the taste, texture, and aroma of each bite.
• Yoga: Yoga combines physical postures with breathing exercises and meditation. It promotes relaxation while also improving strength and flexibility.
• Body Scan: This technique involves mentally scanning your body from head to toe for any areas of tension or discomfort.
• Walking Meditation: This practice involves being fully aware as you walk, paying attention to every step’s sensation without judgment or distraction.
Mindfulness practices do not have to take up large chunks of time; even dedicating just 5-10 minutes per day can yield significant benefits over time:
● Improved focus
● Better stress management
● Enhanced emotional regulation
● Increased self-awareness
● Reduced risk of mental health disorders
In conclusion, incorporating mindfulness practices into one’s daily life has been shown through numerous studies to reduce stress levels significantly, improve cognitive function, promote emotional stability and overall enhance quality of life. By directing our focus onto the present moment rather than dwelling on past regrets or future anxieties we foster an environment conducive for personal growth and well-being.
Role of Professional Therapy in Addressing Trauma-Related Anxiety
Professional therapy plays a pivotal role in mitigating the aftermath of traumatic experiences and managing related anxiety. The therapy, delivered by qualified health professionals, guides individuals through the process of acknowledging and understanding their trauma, thus fostering resilience. In addition to being a safe space where individuals can express themselves freely without fear of judgment, therapy equips them with coping mechanisms designed to alleviate anxiety symptoms.
The therapy approaches, such as Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR), are especially effective in treating trauma-related anxiety. CBT aims at restructuring harmful thought patterns and building self-efficacy, while EMDR helps process traumatic memories and reduce their lingering impact. Both practices have been empirically validated and are widely recognized for their effectiveness in managing trauma-induced anxiety.
Group Support: A Key Tool for Recovery
The healing process from trauma-related anxiety and stress disorders is often a multifaceted journey, where the value of having a supportive environment cannot be underestimated. Group support structures play a pivotal role in this regard. This form of social fabric acts as a powerful tool that fosters an environment of understanding, empathy, and mutual assistance. The collective strength derived from such a setup aids individuals in their path to recovery by instilling hope while underscoring the fact that they are not alone in their struggle.
Regular engagement in group therapy and support-oriented activities facilitates the sharing of personal experiences and coping strategies. Survivors find solace in these shared narratives that depict common struggles and successful triumphs over trauma-induced disorders. In this setting, compassionate communication forms the bedrock of healing. Individuals discover that they can not only receive help but also offer it to others. This process serves to boost self-efficacy and provides a vital platform for cathartic release, contributing significantly to the overall journey of recovery.
Exploring Pharmacological Treatments for Stress Disorders
Pharmacological interventions offer significant promise in the management of stress disorders, acting as one of several pillars supporting holistic treatment plans. They can significantly reduce the severity of symptoms, making it easier for patients to participate in psychological therapy sessions. Various classes of medications are employed in the treatment of these conditions, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), benzodiazepines, and beta blockers, each targeting a different aspect of the disorder.
SSRIs, for instance, are often first-line treatments for stress disorders due to their ability to influence the serotonin system and indirectly regulate mood. On the other hand, benzodiazepines, although highly effective, are typically viewed as a second-line treatment because of the risk of dependency. They function by enhancing the effects of the neurotransmitter GABA, thereby decreasing symptoms of anxiety. Beta-blockers, while perhaps less common, can impede the physical manifestations of stress and anxiety such as a rapid heart-rate. The choice of medication is entirely contingent on the individual’s specific symptoms, their overall health, and their personal response to medication. It must be noted that while these medications address symptoms, they do not cure the disorder, underscoring the importance of concurrent psychotherapy.
Importance of Family and Community Support in Recovery Process
Fostering an environment of understanding, empathy, and support within the family and community can significantly aid an individual’s journey towards recovery. The immediate family can serve as the first line of defense, playing a pivotal role in acknowledging an individual’s struggle and helping them seek appropriate professional interventions. Likewise, the community can integrate various educational programs to dispel misconceptions surrounding mental health, thus promoting a more accepting and supportive atmosphere for the affected individuals.
Additionally, the community can be viewed as an extension of the family- offering a wider network of support. By adhering to a collective approach involving frequent communication, shared responsibilities, and mutual respect, the community can effectively augment the recovery process. Moreover, community-based initiatives like support groups, workshops, and recreational activities can help individuals feel less isolated and more connected to others experiencing similar struggles. Hence, the importance of family and community support in the recovery journey is undeniable.
Maintaining Mental Health Progress: Strategies and Tips
The continuous maintenance of mental health progress can often be as demanding as the initial journey towards recovery. Nevertheless, there are a slew of strategies and tips that could be instrumental in sustaining the advances made. For example, consistently practicing self-care activities can greatly help in maintaining mental well-being. Physical activities such as regular exercise, nutritious diets and adequate sleep substantially contribute to the optimal functioning of the mind. Also, mindfulness practices like meditation and yoga, not only help to reduce stress levels but also promote emotional wellbeing and aid in sustaining mental health progress.
Furthermore, diligent implementation of coping strategies learned in therapy sessions can play a significant role in maintaining mental health improvements. Making time for hobbies and interests, socializing with supportive friends and family, as well as participating in community activities can enhance feelings of connectedness and well-being. It is valuable to remember that recovery is not a linear process, and there may be instances of setbacks. However, being patient with oneself and embracing gradual progress can contribute positively to long-term mental health maintenance. Hence, the key to succeeding in the sustenance of mental health advancement lies in the strategic integration of self-care practices, social support, and professional therapeutic techniques.