Overcoming Seasonal Depression with Local Outdoor Activities in Carneys Point
Understanding Seasonal Affective Disorder
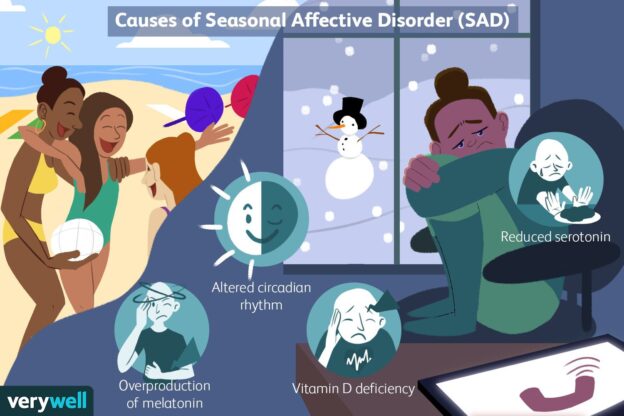
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) is a type of depression that emerges at specific times of the year. Characteristically, it surfaces during late fall or early winter and fades as spring and summer approaches. It operates distinctively from regular depression, as it is linked to changes in seasons and hence, is predictable, reoccurring annually. Fundamentally, it impacts a person’s mood, energy levels, appetite, and overall well-being, aiding in the depletion of the individual’s quality of life.
Triggered by the reduced level of sunlight during the shorter days of the year, SAD causes a dip in serotonin, a neurotransmitter instrumental in mood regulation. Additionally, there is an increase in the production of melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep and is produced in increased darkness, leading to feelings of lethargy and fatigue. The interaction of these phenomena can result in the onset of SAD, with symptoms typically increasing in severity as the season progresses.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Seasonal Affective Disorder
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) is a form of depression that follows a seasonal pattern, often surfacing in the colder, less light-filled fall and winter months. It is essential to recognize its symptoms to seek appropriate help, ensuring overall well-being. Contemporary research has established key symptoms which predominantly encompass a depressed mood most of the day, nearly every day, and a marked loss of interest or pleasure in activities one typically enjoys. These core symptoms are usually accompanied by increased sleep, appetite or weight changes, and low energy levels.
Some individuals may also exhibit other distinctive signs such as feelings of worthlessness, guilt, hopelessness, or troubles concentrating and making decisions. Additionally, recurrent thoughts of death or suicide is a severe symptom that requires immediate medical attention. It’s worth noting, despite these overlapping symptoms with major depressive disorder, Seasonal Affective Disorder is unique as it usually subsides with the onset of Spring and Summer, correlating with increased daylight hours. This temporal association underlines a significant connection to environmental factors playing a role in SAD manifestation.
The Impact of Outdoor Activities on Mental Health
In the realm of mental health, the significance of outdoor activities cannot be overstated. Communion with nature and exposure to natural light provide essential benefits for the human mind. The former fosters a deeper connection to the environment, effectively reducing levels of stress and anxiety. Exposure to natural light, on the other hand, regulates sleep patterns by influencing the body’s production of melatonin, which can notably enhance personal mood and energy levels.
Additionally, these activities typically entail some degree of physical exertion, which also plays a crucial role in mental wellbeing. Exercise aids in releasing endorphins, often referred to as ‘feel-good hormones’, that can help alleviate symptoms of depression and improve mental health conditions. Thus, it’s clear that the psychological benefits derived from outdoor recreational activities are numerous and substantial in boosting mental health.
Benefits of Engaging in Outdoor Activities
Engaging in outdoor activities offers a range of both physical and mental benefits contributing to overall well-being. Activities such as hiking, fishing, running, or simply spending time in nature can exercise the body, promoting cardiovascular health, building muscular strength, and enhancing coordination and balance.
From a mental perspective, being amidst nature has been consistently linked to decreased levels of stress, increased feelings of happiness, and improved concentration. Exposure to green spaces can act as a natural mood-enhancer, providing a much-needed break from the daily grind and facilitating psychological relaxation. Outdoor activities also promote socialization and offer opportunities for creating meaningful connections with other individuals, which are integral components of emotional health.
Exploring Outdoor Recreation Options in Carneys Point
Carneys Point, a versatile region located in Salem County, New Jersey, brims with wide-ranging opportunities for engaging in outdoor activities. With its expansive greens, rambling river, and bustling sports facilities, this area offers a comprehensive palette of recreational pursuits for all tastes and interests. It is a promising locale for individuals seeking to promote their mental well-being through indulging in refreshing outdoors.
Forest walks and hiking can be explored in the stretching woodland areas, which offer scenic trails and beautiful flora and fauna sightings. For water enthusiasts, the Delaware River is a prime spot for fishing and boating adventures. In terms of sports, the numerous local parks are equipped with facilities for soccer, baseball and other group activities that foster both physical health and a sense of community. With such diverse options, Carneys Point serves as a versatile platform for engagement in outdoor recreation.
Forest walks and hiking: A breath of fresh air for Seasonal Affective Disorder
Engaging in forest walks and hiking activities provide mental health benefits beyond the mere physical exertion involved. These exterior pursuits do not only awaken the senses to the beauty, sounds, and scents of nature, but also serve as a form of eco-therapy – a term used to define the process of improving mental and emotional well-being via interaction with the natural environment. According to numerous research studies, this type of immersion in nature can reduce stress hormones, and improve mood, focus, and concentration. The tranquility and solace that a forest environment provides have been reported to be especially helpful in mitigating feelings of anxiety and depression associated with Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD).
In addition to the mental health benefits, regular hiking or forest walking are also known to provide remarkable physiological advantages. These range from improved cardiovascular health, enhanced respiratory performance, better balance, and increased strength and endurance. Furthermore, forest walks could serve as a viable alternative for those who may find traditional gym environments intimidating or monotonous. The mesmerizing beauty of nature trails and the rhythmic cadence of footsteps against a path could lead individuals into a meditative state, giving them a chance to disconnect from digital distractions and reconnect with their inner selves. As such, forest walks and hiking should be considered not just as leisure activities, but as essential rites in the pursuit of holistic wellness.
Fishing and Boating: Embracing Water Activities
Fishing and boating are among the most popular water-based activities that hold significant mental health benefits. The calming presence of water can provide individuals with a serenity that can reduce stress levels, evoke relaxation, and improve overall mood. Participation in these activities not only offer the benefits of physical exercise but also harness the tranquility of nature to improve mental wellbeing.
Engaging in fishing requires patience and quiet focus, thereby promoting mindfulness, which staves off anxiety and depression. On the other hand, boating, whether leisurely or competitive, drives the essence of camaraderie, teamwork, and determination, which can boost self-esteem and team spirit. The feeling of the cool wind in one’s hair and the rhythmic lapping of water against the boat hull are calming stimuli that are known to provide respite from stress and induce relaxation.
Engaging in outdoor sports is a well-established way to enhance both mental and physical health. Such activities not only cultivate a sense of teamwork among participants, but they also present robust opportunities for physical fitness. Team sports like soccer, baseball or ultimate frisbee, which promote collaboration and mutual understanding among players, offer a structured setting to enhance social skills while fostering positive competition.
On the physical fitness front, outdoor sports effectively address multiple fitness components, including cardiovascular endurance, muscular strength, flexibility, and body composition. In particular, activities such as cycling and swimming are low-impact sports that boost cardiovascular health and facilitate effective weight management. These combined benefits of outdoor sports make them an incredibly effective tool in managing mental health conditions like Seasonal Affective Disorder.
Successful Stories: How Locals Improved their Mood through Outdoor Activities
Nancy Smith, a resident of Carneys Point for over two decades, shares her transformative journey with outdoor activities. Diagnosed with Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD), she felt desolate and experimented with several treatments with minimal improvements. However, things turned around when she attended a community outdoor activities program on a casual suggestion by a friend. Starting with basic gardening and gradually progressing to hiking, she noticed a definitive improvement in her mood and overall health. Her personal accomplishments are truly inspiring as she now leads a hiking group in her community and actively encourages and educates people on the benefits of outdoor activities.
Similarly, the community has witnessed admirable improvements in the life of a school teacher named Peter Johnson. A person of solitary lifestyle by preference, the chilling winters took a toll on his mental health triggering the symptoms of SAD. He decided to challenge himself by joining a local ice hockey club, despite never having skated before. It was a struggle for him at first, but as time passed, he not only observed stark improvements in his mood swings but also developed a newfound passion for the sport. Today, Peter is a pivotal part of the team, and he actively engages in promoting the sport as a means to counter SAD. These instances serve as a testament to the fact that outdoor activities can indeed play a significant role in combating seasonal affective disorders.
Tips for Staying Active and Positive During the Winter Months
The onset of winter brings shorter days and colder temperatures, which can significantly affect an individual’s mood and overall wellbeing. To counteract this, maintaining an active lifestyle and preserving a positive mindset becomes essential. Engaging in any form of physical activity not only boosts your physical health but also improves your mental state by stimulating the production of endorphins, known as ‘happy hormones.’ Be it a home workout session, a run around the block, or a winter sport, ensuring regular exercise can significantly contribute to combatting signs of lethargy and gloominess often associated with Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD).
Simultaneously, adopting a positive mindset is equally crucial. Incorporating mindfulness exercises and meditative practices into your daily routine can greatly reduce stress levels and promote a more optimistic outlook. Other cognitive strategies include setting small daily goals and celebrating these achievements, practicing gratitude, and maintaining virtual or in-person social interactions. Remember, consistently following these tips won’t completely eliminate the challenges one might face during the winter season, but they certainly can provide the necessary tools for managing and reducing the impact on one’s psychological health.