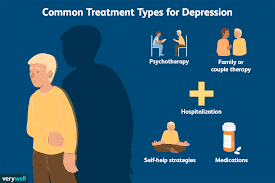
Understanding Depression: Symptoms and Causes
Depression is a common and serious mood disorder that pervasively affects how an individual feels, thinks, and handles daily activities. Characterized primarily by a persistent feeling of sadness or a lack of interest in outside stimuli, depression, also known as major depressive disorder or clinical depression, can lead to a variety of emotional and physical problems. It’s not uncommon for people suffering from this disease to have difficulty in performing normal day-to-day tasks. In severe cases, depression can instigate thoughts of suicide or self-harm.
The roots of
Misery are multifaceted, encompassing a blend of biological, psychological, and social sources of distress. The interplay of these factors varies from person to person. A family history of depression can lead to a higher susceptibility to the condition due to genetic factors. However, adverse life events such as a bereavement, financial woes, or a relationship breakup can also prompt episodes of depression. Evidence suggests psychological make-up also plays a substantial role, as people with certain personality traits are more prone to depression. These include low self-esteem, being overly dependent, self-critical or pessimistic.
Exploring Holistic Approaches to Manage Depression
Holistic approaches to depression management seek to address the individual’s wellbeing as a whole, rather than focusing solely on alleviating the specific symptoms of the disease. This involves an integrative strategy that considers the physical, mental, emotional, social, and spiritual aspects of the individual’s life. Notable holistic approaches include mind-body therapies, dietary modifications, physical activity, and various forms of psychotherapy. These strategies aim not only to reduce the severity of depression symptoms, but also to enhance the individual’s overall quality of life, resilience, and coping mechanisms.
Mind-body therapies such as yoga, meditation, and mindfulness have been shown to reduce stress, improve mood, and enhance cognitive function, all of which can be beneficial in managing depression. Dietary modifications and physical activity, on the other hand, can help improve physical health, boost mood, and increase energy, further aiding in depression management. Psychotherapies, especially
cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can be particularly effective in helping individuals alter negative thought patterns and develop more effective strategies for coping with life’s challenges. These holistic approaches, when used in conjunction with medication (when necessary) and under the guidance of healthcare professionals, can provide more comprehensive and long-lasting results for individuals with depression.
The Role of Yoga and Meditation in Treating Depression
The discipline of yoga, a practice that blends physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation techniques, has demonstrated promising results in treating the symptoms of depression. Regular yoga practice has been shown to improve mood, enhance relaxation, and reduce levels of stress, factors all meaningful in managing the distress of depression. Through the encouragement of mindfulness and a connection between mind and body, yoga can foster an enhanced sense of well-being, thus acting as an effective therapeutic tool.
Meditation, on the other hand, often incorporates mindfulness-based techniques to cultivate a focused attention on the present moment. It’s predicated on the notion of creating a mentally clear and emotionally calm state, reducing overstimulation and drawing out inner tranquility. Depression, known to thrive in the frenzy of a disjointed mind, can be mitigated by habitual meditation. This practice, serving as a natural antidote to the anxious ruminations that often accompany depression, reinforces mental resilience and promotes emotional balance.
Importance of Nutritional Therapy in Managing Depression
Incorporating dietary modifications identifies as a potent strategy in managing the symptoms of depression. The role of essential nutrients in enhancing mental wellbeing has gained considerable momentum in the discourse towards non-pharmacological interventions for depression. Magnesium, Omega-3 fatty acids, L-theanine, and several B-vitamins have been associated with improved mood and reduced incidents of depressive episodes, providing a significant insight into the potential of nutritional therapy as an auxiliary treatment option for depression.
To optimize the benefits of nutritional therapy, individuals need not only focus on incorporating nutrient-rich foods into their diet but also evaluate their overall eating patterns. There are compelling links between obesity, high-sugar consumption, and depression. Balancing nutrient intake, reducing processed foods, and aligning eating patterns with body’s natural circadian rhythms can support not just physical health, but also mental health, hence pushing nutritional therapy to be more than a footnote in the broader clinical conversation on combating depression.
Changing Lifestyles: The Impact of Physical Activity on Depression
Physical activity is touted as a primary method for not only improving physical health but mental health as well. Numerous studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of regular exercise in reducing symptoms of depression. Exercise triggers the production of endorphins, the body’s natural mood elevators, thereby promoting feelings of happiness and relaxation. Moreover, physical activity improves self-image and cognitive function, enabling individuals to develop a healthier perspective on themselves and the world around them.
The kind of activity doesn’t necessarily have to be rigorous for the benefits to take effect. Walking, yoga, cycling, or any form of physical exertion that elevates the heart rate regularly for at least 30 minutes is adequate. However, it is imperative for individuals suffering from depression to understand this: while physical activity can notably alleviate symptoms of depression, it doesn’t replace professional mental health treatment. It should be seen as a compliment to prescribed therapies. The multi-pronged treatment approach ensures a holistic healing process, granting the individual a better fighting chance against depression.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy: A Non-Pharmacological Approach
Cumulatively, depression significantly impedes daily functioning, leading to a diminished quality of life. As part of a comprehensive treatment plan, Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is regarded as an effective non-pharmacological approach. CBT focuses on addressing the thought patterns and behavioral tendencies that perpetuate depressive symptoms, thereby aiding in their relief. This psychotherapeutic technique is constructed on the idea that negative interpretations of events exert a strong influence on one’s emotional state. By applying CBT, patients are equipped with the tools to discern and combat these damaging thought patterns.
CBT, unlike some other forms of therapy, typically confines itself to the present. It empowers patients to cope with their current problems rather than delving into past trauma or events. Numerous studies have attested to the efficacy of CBT in decreasing depressive symptoms and preventing relapse. It fosters cognitive restructuring, which involves reorganizing thoughts in a healthier, more positive manner. With specific strategies like mindfulness, patients learn to focus on the present moment rather than dwelling on past events or anticipating future anxieties. As such, CBT offers an empowering and practical approach to managing depression.
Art Therapy: Using Creativity to Combat Depression
Art therapy holds a unique place in
depression treatment by engaging individuals in a creative process for healing. It has proven to be a valuable tool, offering an avenue to express feelings or experiences that may be difficult to communicate through words. This form of
therapy may include various art mediums such as painting, sculpting or drawing that can help unravel thoughts and emotions beneath the surface. The creation process can provide a sense of accomplishment and control, which can often counter feelings of helplessness associated with depression.
Furthermore, unlike traditional talk therapies, art therapy provides an enriched platform for individuals to explore their feelings. Through connecting with the subconscious mind, it can reveal insights that may not be apparent or are too painful to confront in normal daily life. The therapist can facilitate individuals to interpret the symbolism in their artwork, aiding the understanding of the emotional factors contributing to their depression. Through this artistic process, individuals can develop emotional resilience and a self-awareness, sparking the path towards healing and recovery.
Role of Herbal Remedies and Supplements in Depression Management
In the realm of depression management, herbal remedies and supplements have played an increasingly significant part, presenting as natural alternatives to pharmaceutical treatment. Several research studies indicate noteworthy connections between certain natural substances and improved mental health outcomes. These remedies primarily include botanicals like St. John’s Wort, Saffron, SAM-e, and Omega-3 fatty acids. Their efficacy is often measured in varying degrees, with some individuals reporting substantial improvements in mood and reducing symptoms associated with depression. However, it is important to remember that while these supplements can be effective, they are not universally successful and should not replace other treatment methods without medical guidance.
The application of these remedies happens under the guidance of a healthcare professional to assure the right dosage and monitoring of potential side effects. As natural as they might be, these herbal remedies and supplements can interact with other medications or health conditions, potentially causing adverse reactions. Therefore, individuals must engage in a deeply informed and cautious approach when considering their use as a part of depression management strategy. Recent years have seen an uptick in the interest surrounding these natural supplements and their potential benefits for mental health, but it is crucial to underscore that further research is needed to fully understand their role and efficacy in treating depression.
Importance of Social Support and Community Involvement
Maintaining strong social connections and active involvement in community activities can play an instrumental role in managing depression. Individuals plagued with this mental health disorder often find themselves feeling isolated or misunderstood. However, social support systems act as buffers, providing encouragement, care, and a sense of belonging that can significantly alleviate feelings of loneliness and despair. The emotional comfort that effective social support groups offer can affect individuals positively, helping them recover more swiftly.
Community involvement can also serve as a powerful tool in combating depression. Participating in communal activities can foster a heightened sense of purpose and belonging. It allows individuals to focus on tasks outside of their struggle, providing them with respite, and granting them an opportunity to connect and share experiences with others who might be facing similar situations. Moreover, it creates a platform for building social skills, boosting self-confidence and self-worth, all of which are crucial facets in managing depression.
Monitoring Progress: Ensuring Effectiveness of Adopted Therapies
As one ventures on the journey of managing depression, it is crucial to monitor the progress and ensure the effectiveness of the adopted therapies. This involves regular check-ups with healthcare providers, self-assessments, feedback from loved ones, and, potentially, the use of certain technological tools. These elements are not only critical to assess the effectivity of the chosen treatments but to also make necessary adjustments when required. By keeping a close eye on the progress, individuals can identify which aspects of their treatment plan are working and which may need modification.
Amidst this monitoring process, the data collected can provide invaluable insight into the individual’s coping mechanisms and their responses to different therapeutic strategies. With the help of professionals, this data can be analyzed to fine tune therapy plans and potentially introduce new approaches that may benefit the individual. While the monitoring process may seem taxing, it is crucial for it ensures that the adopted therapies yield the anticipated positive impacts. This consistent oversight is the key to comprehensive and successful management of depression.